Industry 4.0 and its Implications in Process Industry
Industry 4.0 has many synonyms. It is referred to as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Digital Revolution, and the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It doesn’t matter how we define it; Industry 4.0 is all set to bring in revolutionary changes to the process industry in the coming years.
Industry 4.0 defines the Smart factory. Industry 4.0 aims at embracing the ongoing digital transformation development and evolution of connectivity. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud technologies and cognitive computing to provide intelligent autonomy to the Manufacturing process, thus enhancing efficiency manifold and optimising the production process.
It is an amalgamation of people, processes, workflows, services, IT systems, production equipment and other physical assets that generate data during the processes of manufacturing. Industrial IoT helps various departments, manufacturers, suppliers and consumers alike provide increased automation, improved communication and monitoring, along with self-diagnosis and new levels of analysis for improved productivity.
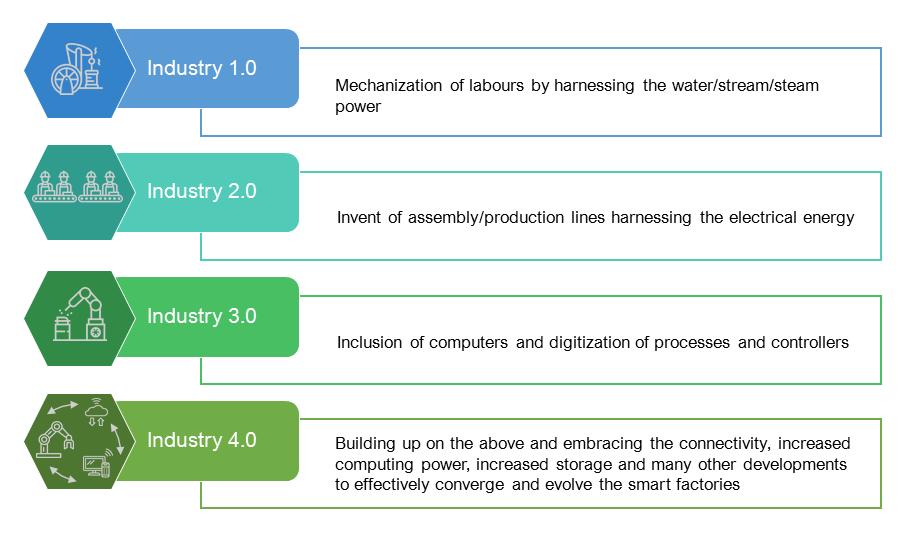
We are currently witnessing the transformation of Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0. The 3rd Industrial Revolution focused on computerization and automation of processes, whereas, Industry 4.0 builds above it by embracing connectivity, increased computing power, increased storage and many other developments to effectively converge and evolve the smart factory. IIoT presents a better economic scenario, faster time to market, enhanced work quality and streamlined decision making. Today, Product Engineering companies in the market offer various Industry 4.0 services that help Manufacturing firms to realise their Automation Strategies in a short period of time. Industrial Automation solutions such as design and development Industrial Sensors control systems and gateways, integrating legacy systems and application development to developing integrating these systems to enterprise server to provide a seamless IoT enabled solution for manufacturing / production line automation.
KEY ENABLERS OF INDUSTRY 4.0
Let’s look at the key facilitators of this digital transformation called Industry 4.0.
- IoT [Internet of Things] helps embedded systems to communicate through centralized devices. This involves adding various Sensors or extending the existing sensors to connect them to centralized servers via IoT Gateways or existing devices enabling the direct communication from the sensor to server (cloud or centralized) and thereby enable data collection from the real-time systems.
- Big Data analytics is the process of analysing large quantities of data to establish patterns, drive statistical relationship and thereby model the data to be able to make meaningful decisions to influence the process/business. The analysis could include information such as marketing trends, consumer preferences, mean time to failure, mean-time between failures, estimation the failure based on the current health etc. in order to make informed decisions. Big data analytics is effective in lean inventory, just-in time manufacturing, predictive maintenance where it helps to monitor and control the production process to attain maximum efficiency. Big Data analytics plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0 as it is a vital enabler of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Machine Learning – a subset of AI [Artificial Intelligence] – enabled capability of machines to autonomously perform tasks and constantly update themselves from experience with minimal human intervention. The process of learning begins with various data gathered and analysed previously, observations, instructions given to the machine over a period and decisions made earlier with or without human intervention.
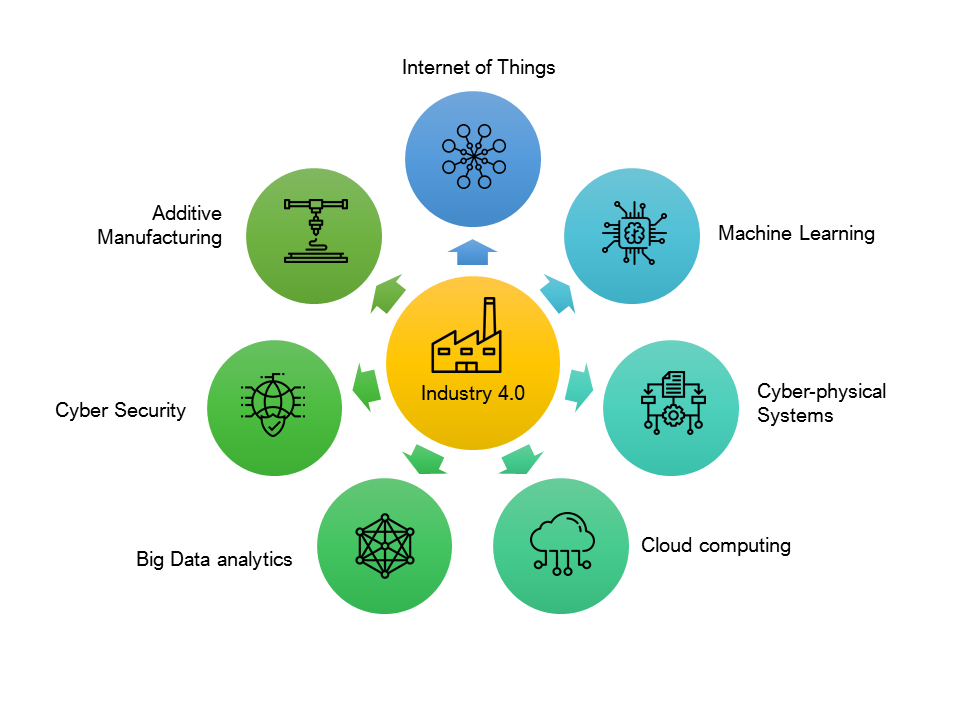
- Cyber-Physical System [CPS] refers to smart factory environment with controllers (or Robots) applying the AI/ML, on the data gathered using the sensors in storage, to autonomously manage devices in an IoT ecosystem and thereby ensuring that the operations are monitored, coordinated and controlled for optimum output. Various algorithms analyse the physical environment and the data generated by physical assets to trigger a decision that will make a change in the process or in the ecosystem. CPS enable factories and manufacturing plants to respond to such changes easily. CPS have broad applications that include manufacturing, automotive systems, medical devices, assistive technologies, Traffic/Parking Management, process control, power generation and distribution, HVAC Automation, water management systems, Asset management, distributed robotics, Military and Aerospace and more.
- Cyber security, without a doubt is one of the key enablers of Industry 4.0. With an increasing dependency on technology and digitization of data, it is important to insure protection and privacy of this infrastructure and data. Constant improvement in cybersecurity is crucial in Industry 4.0 as any kind of threats/attacks on your assets will lead to production downtimes, communication / production equipment malfunctioning, data leakage, and even faulty products that will further lead to financial loses and reputational issues.
- Cloud computing: We spoke about automation, IoT, cyber-physical systems etc. Cloud Computing enables a seamless communication and coordination across all these factors systems. –Cloud computing powers this hyper-connected environment enabling easy access to all IT infrastructure and other IoT enabled physical platforms. Cloud is driving the change by providing a flexible, scalable and cost-effective platform, yet with unprecedented computation, storage and networking capabilities for organisations.
- Additive manufacturing will be the next big enabler of Industry. 4.0. Also referred to as 3D printing, Additive Technology is made possible by the advent of digitalization in manufacturing processes. 3D printing will heavily enable creation of lighter and stronger components, particularly for spare parts and prototypes. . . Decentralized 3D facilities could also help reduce transport distances and inventory maintenance costs.
ADVANTAGES OF INDUSTRY 4.0
Industry 4.0 helps companies evolve and survive in a competitive and dynamic environment. With machine learning, predictive analysis and big data you can tackle potential problems before they turn to threats. Technology makes work easier and serves as an attractive way to do tasks. Industry 4.0 ensures increased efficiency and minimises human error due to better process control Thanks to Big Data, AI and Machine Learning. Industry 4.0 enabling quick and clear decision-making, trims cost, boosts growth and increases profits.
CONCLUSION
Industry 4.0 is set to be a key ingredient for the sustenance of any organization in the process Industry. To remain competitive, organization’s need a system that can manage the demands of organisation, customers, investors and other stakeholders in a seamless way, and this will be enabled by Industry 4.0. Many organizations are working to adopt these technologies and upskilling their current workforce to adapt to the altered work responsibilities and to recruit additional workforce with the right skills. Organizations face á formidable challenges in the adoption of these new technologies due complex implementation process, lack of clearly defined standardized processed and migration of legacy systems.
Mistral is a product engineering company that can support you through the entire process from designing customized industrial products to developing custom applications integrating these products and legacy applications via the enterprise server to provide a seamless Industry 4.0 enabled solution for the process industry.




