IoT Testing Processes for Building Robust IoT System
Introduction
Internet of things (IoT) as we all know is an ecosystem of systems, sensors and devices which are connected over a network enabling communication among them. IoT devices not only include computers, laptops, tablets, smartphones, but all the devices that incorporate chips that can connect to the internet to communicate and gather information. It is a platform which allows users to manage data and control the connected devices remotely. According to Gartner, approximately 8.4 billion things were connected in 2017, and the figure is expected to rise to 20.4 billion things by 2020. And, according to IDC, there will be 41.6 billion connected IoT devices, or “things,” generating 79.4 zettabytes (ZB) of data in 2025.
The range of existing and potential Internet of Things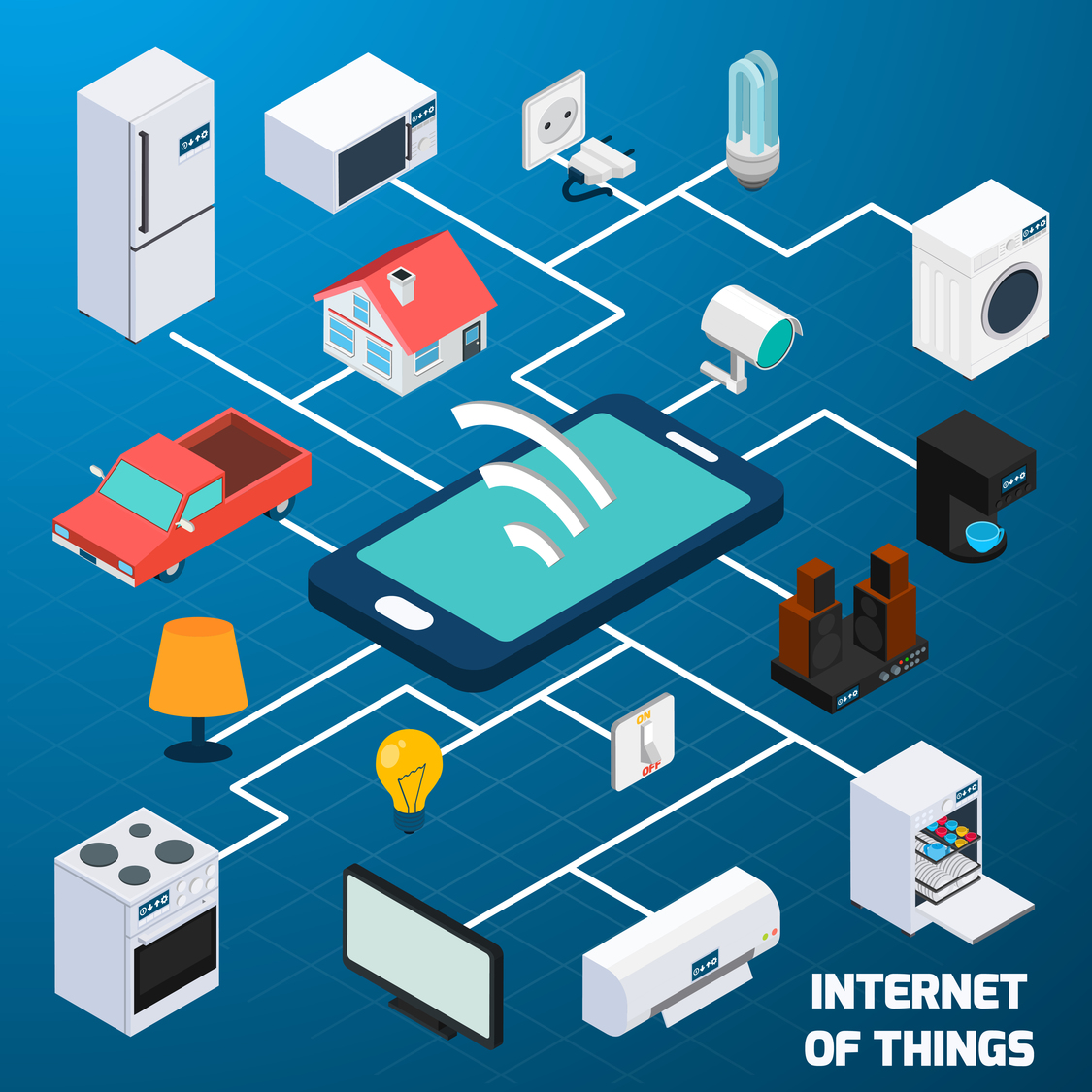  devices is enormous. With the current focus on smart cities, smart homes, and smart gadgets, it is expected that people, businesses, and the government will be tremendously impacted by IoT. It is also expected that the smart devices such as coffee machine, toasters, toys, washing machine, automated smart doors, refrigerators, smart switches, and many others will be connected to the network and communicated via smartphones. All of these devices are enabled with either via Bluetooth, WiFi, RFID or Z-Wave to connect with each other seamlessly. Here are a couple of scenarios on how IoT could change your life:
devices is enormous. With the current focus on smart cities, smart homes, and smart gadgets, it is expected that people, businesses, and the government will be tremendously impacted by IoT. It is also expected that the smart devices such as coffee machine, toasters, toys, washing machine, automated smart doors, refrigerators, smart switches, and many others will be connected to the network and communicated via smartphones. All of these devices are enabled with either via Bluetooth, WiFi, RFID or Z-Wave to connect with each other seamlessly. Here are a couple of scenarios on how IoT could change your life:
Example 1 – When you return from a jog and park your bicycle in the garage, the sensors available inside the garage detects the opening of the door and sends a notification to turn on a coffee maker and microwave via IoT.
Example 2 – On parking your car in the allocated area of office space, the sensor sends the notification through IoT to turn on the air conditioner, cabin lights and enables a perfect start of the day.
En route to integrating more than 20+ billion devices into various verticals such as Agriculture, healthcare, smart homes, manufacturing, retail, etc., within the next few years, IoT development is expected to increase the scope of Internet of Things testing significantly. As the number of connected devices increases the challenges for software developers and testers also increases. In this article, we will cover some of the testing processes required to test IoT devices.
IoT Testing Processes
Before releasing any product in the market, it is of utmost important to test the function of all devices according to the standards set for it. IoT systems, taking up the centre stage in the consumer space, have to go through many important phases of testing. Below listed are few IoT testing processes.
- End-user application testing
It is essential to ensure that all the connected devices such as smartwatches, automated doors, vending machines, industrial robots, etc., work seamlessly to provide a gratifying user experience. With a myriad of devices connected through the internet of things, usability testing becomes at most important.
- Security Testing
This is the top priority area in IoT testing process as all the devices are provided with IP addresses and can transfer data over the network. The spread of the IoT has been a boon for hackers who can easily target these devices. Hence, it is crucial to test all the devices to eliminate vulnerabilities and maintain the integrity and security of data. The prime area of focus in security testing includes data protection, device identity and authentication, data encryption/decryption and data storage in the cloud.
- Connectivity Testing
As all the devices in an IoT system are connected through the network, they must be available constantly and also ensure seamless connectivity with the user. There are chances of any of these connected devices going offline. Thus, it becomes crucial to check the behaviour of the device during offline mode. A warning message has to be sent to the end-user if the device is offline or does not have a unified communication with the user.
- Performance Testing
IoT devices continuously generate a huge amount of data. Performance testing ensures that these devices can work seamlessly without any interruptions. IoT performance testing is a complex and time-consuming process that ensures the development of a robust IoT system. This testing process involves testing of multiple components and endpoints, network communication, internal computation, timing analysis, load testing, data volume, velocity, variety, and accuracy and scalability
- Compatibility Testing
An IoT ecosystem has a complex architecture as there are numerous devices which can be connected through it. All of these devices are configured with various hardware and software systems. This makes it important for a tester to perform a compatibility test between all the combinations of these connected devices to ensure seamless performance.
- Pilot Testing
Verifying the IoT system before the full deployment of the system is important as it helps the tester in identifying defects in the early state. In this IoT testing process, the entire system or a single component is tested under real-world operating conditions to check if it is ready for full-scale implementation.
- Regulatory/Compliance Testing
When it comes to IoT, regulatory and compliance challenges are likely to grow. In this testing process, compliance of IoT applications for OFAC, HIPPA, GDPA, FDA, FCC, etc is determined. A regulatory test is done on the internal and external system to check if all the specified standards set by IEEE or W3C are met. The main objective of this test is to ensure that the system meets the standards, laws, policies, procedures, and guidelines after every development phase.
- Upgrade Testing
All the Firmware, Hardware, OS, Devices used in the IoT systems will need to get upgraded as the technology advances. So, it becomes important for testers to perform a thorough regression testing of all the connected devices in real-time before releasing upgrades to the end-users, keeping all the above testing processes in mind.
- Data Integrity Testing
Devices in the IoT system interact with each other and a lot of data exchange takes place. Hence, it is important to check the data integrity of IoT systems where the quality of data, accuracy, format, compatibility, and sanctity of data is tested. The data is validated from various devices, database, gateways and IoT servers.
Conclusion
An IoT system consists of Sensors, Applications, Network and Datacenters. Therefore, it becomes very important for the Testing team to determine the various type of testing required to test different IoT elements. And, depending on the system or architecture involved, the IoT testing approaches might vary. It is very important for a tester to test the system using a Test-As-A-User (TAAS) approach, rather than testing based on the defined requirement. Using a TAAS approach helps to deliver a bug-free solution with improved UX to the end-user.
Mistral is a trusted IoT Service Provider, past 20 years, offering a range of Internet of Things services to help you design and implement IoT device designs and IoT Gateway Devices to help realize your strategy. By ensuring interoperability, connectivity, scalability, and stability among various IoT components to form a healthy IoT ecosystem, Mistral, your IoT service provider offers a range of Internet of Things Services and solutions that shorten the time-to-market for our customers.




